WebGME HFSM
WebGME App for creating Executable Heirarchical Finite State Machines (HFSMs). Contains metamodel, visualization, simulation, and code generation for Heirarchical Finite State Machines (HFSMs) following the UML State Machine specification, see Wikipedia UML State Machine, another reference, and the UML specification.
A public server running this project can be accessed at:
Please see the WIKI for further information, including links to relevant Youtube Videos and specific pages about development process and such.
Table of Contents
Features
- Complete modeling of State Machines following the UML specification including:
- States with Hierarchy
- Events
- Internal Transitions
- External Transitions
- Local Transitions
- Choice Pseudostates
- Deep History Pseudostates
- Shallow History Pseudostates
- Initial States
- End States
- Interactive model creation
- In-model interactive simulation of the HFSM
- In-model code attribute editing for the HFSM
- Model transformation plugin to produce executable C++ code from the HFSM (with more languages coming soon!)
Description
This repository contains the plugins, decorators, and visualizers (all of which are WebGME Components) and the base and example seeds for creating HFSMs with embedded c/c++ code in each state. The WebGME app utilizes the CodeEditor to allow users to edit the code for the model as if it were part of an IDE.
Together these components and (meta-)modeling environment make up the State Machine Domain for WebGME.
The Base seed contains just the Meta definitions for the projects and HFSMs following the UML State Diagram specification and the Samples Seed contains a project with three different HFSMs: simple, medium, and complex.
HFSMs are trees, where a state may have zero or more substates.
In this modeling paradigm, Projects can contain any number of State Machines.
State Machines have the following attributes:
Includes: include statements for the HFSM, will be at the top of the generated headerInitialization: intialization code run at the beginning of the HFSM, before any of the state initialization code.Declarations: variable/function/class declarations within the HFSM'sStateMachinenamespace, will be within the generated header fileDefinitions: variable/function/class definitions within the HFSM'sStateMachinenamespace, will be within the generated source file
Getting Started
Setting up the WebGME-HFSM Server
Dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/finger563/webgme-hfsm
cd webgme-hfsm
npm install -g bower # needed for extra package management
npm install # installs the required packages for webgme-hfsm
npm start
Which will run the WebGME-HFSM server on PORT 8081 of your local machine, accepting connections on all IP addresses available to it.
Note: this requires a mongodb instance running on the machine, which can be started with:
mongod --dbpath ${path you want for your database}
Once the server has been started, you can navigate (in Chrome) to
localhost:8081
where the server is running. Create a WebGME project there from either the base or the examples seed.
Creating a HFSM
Once a webgme project has been opened, creat a new HFSM project by dragging in a new component from the left panel.
Double click on the project and then drag in a new HFSM component.
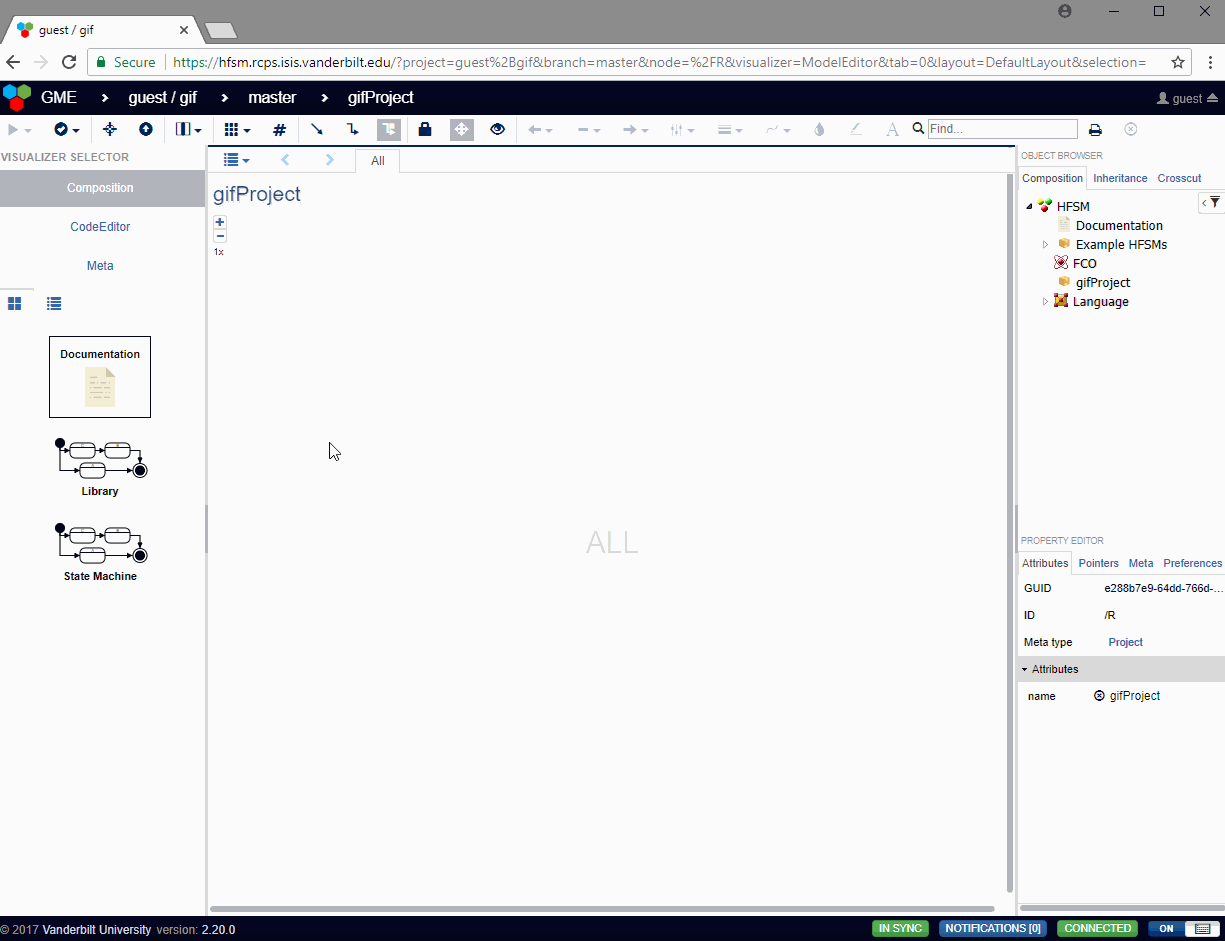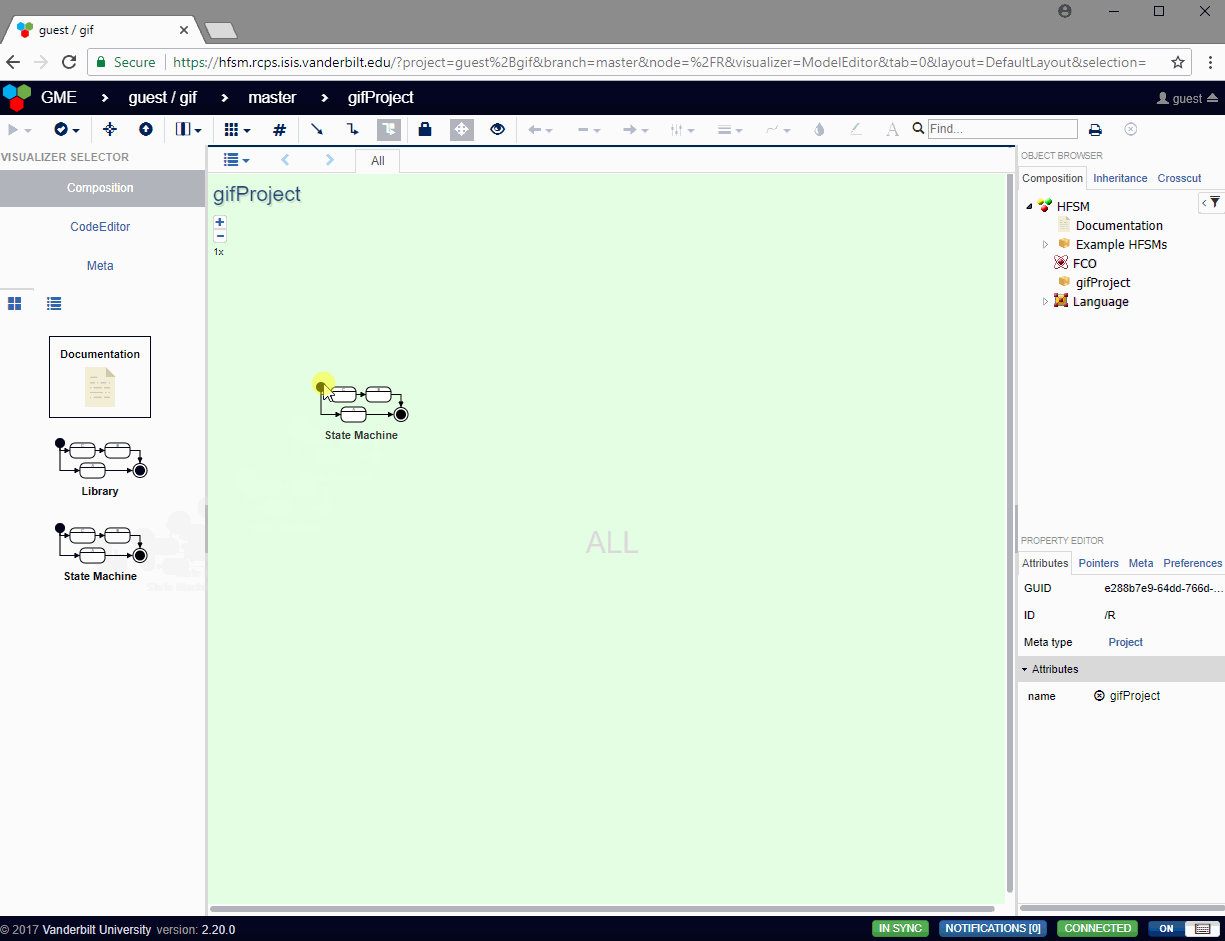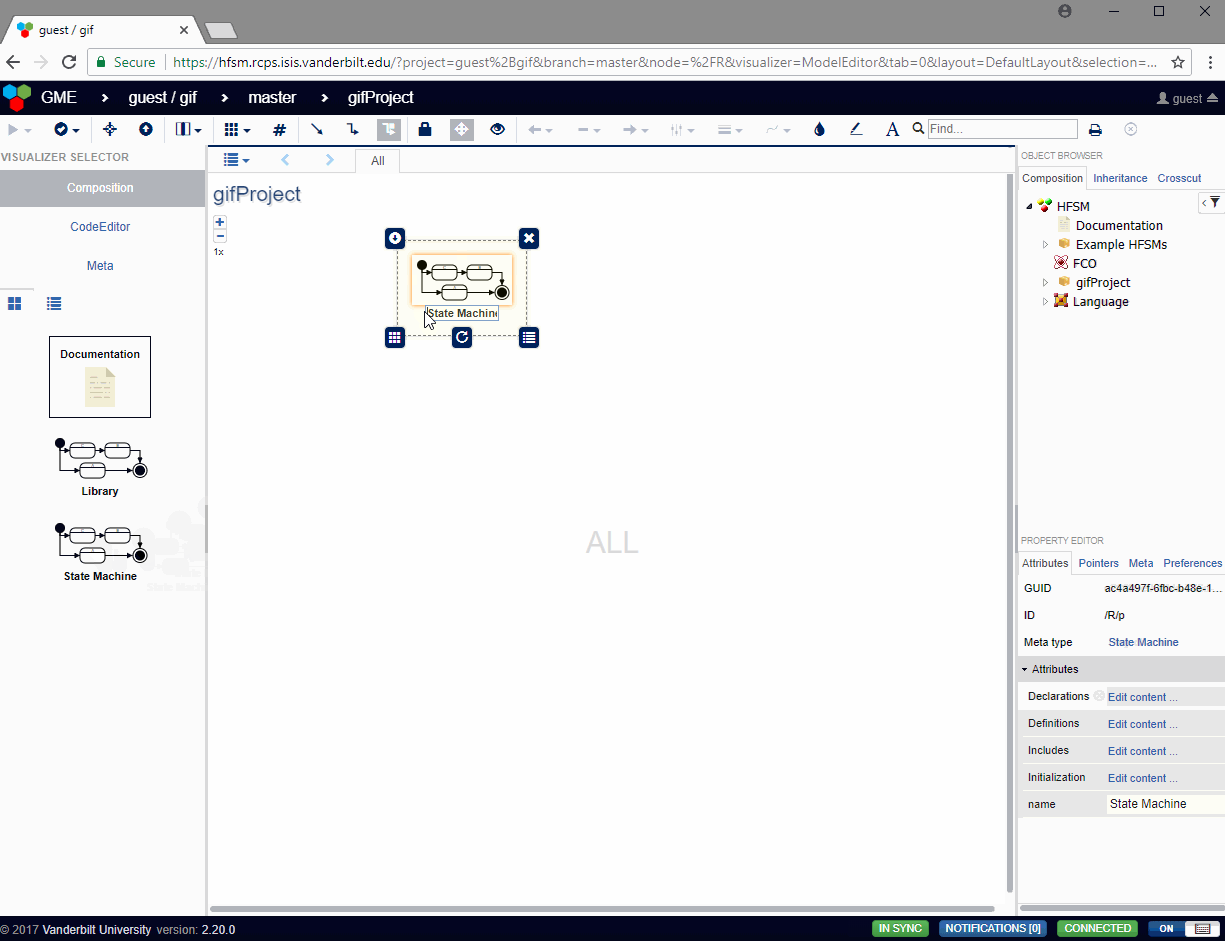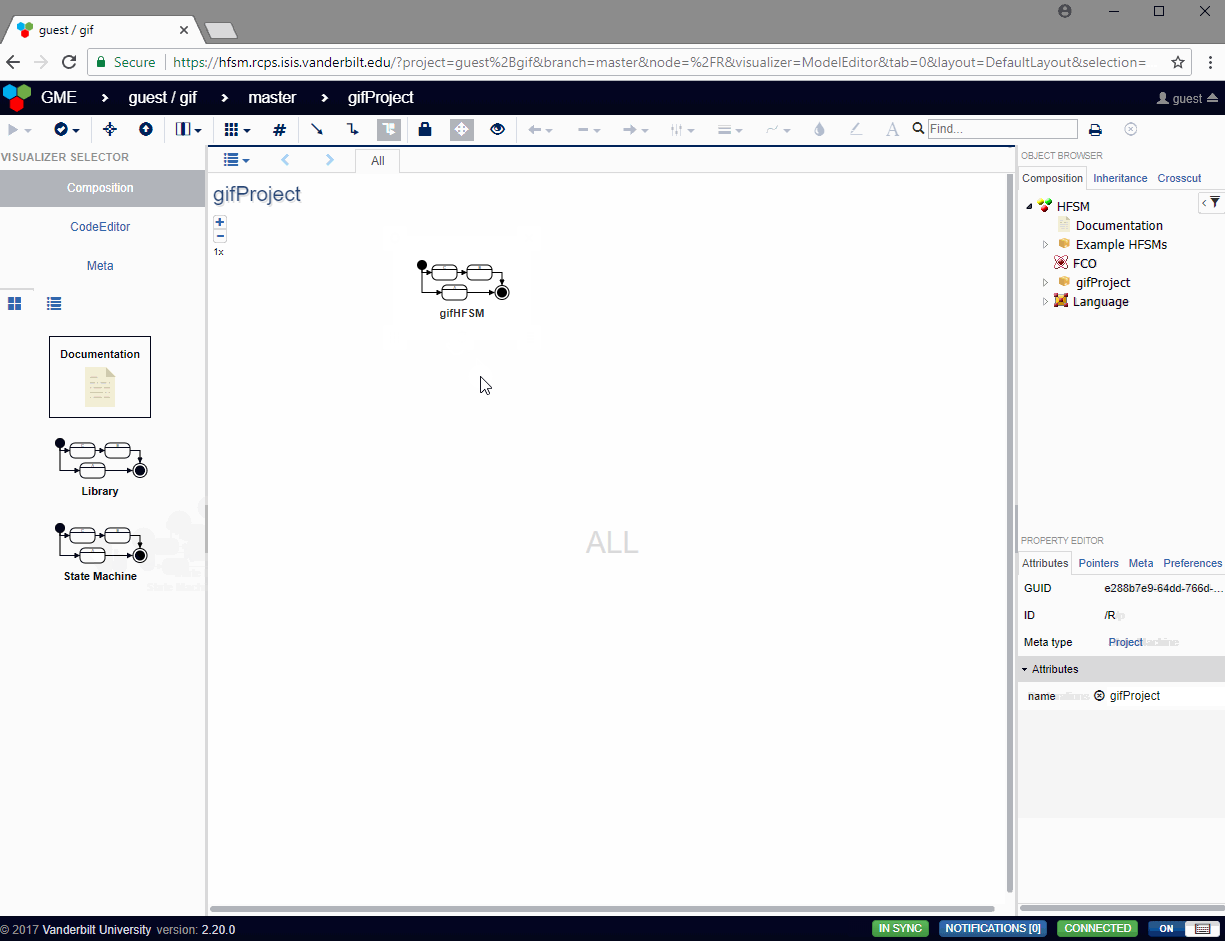
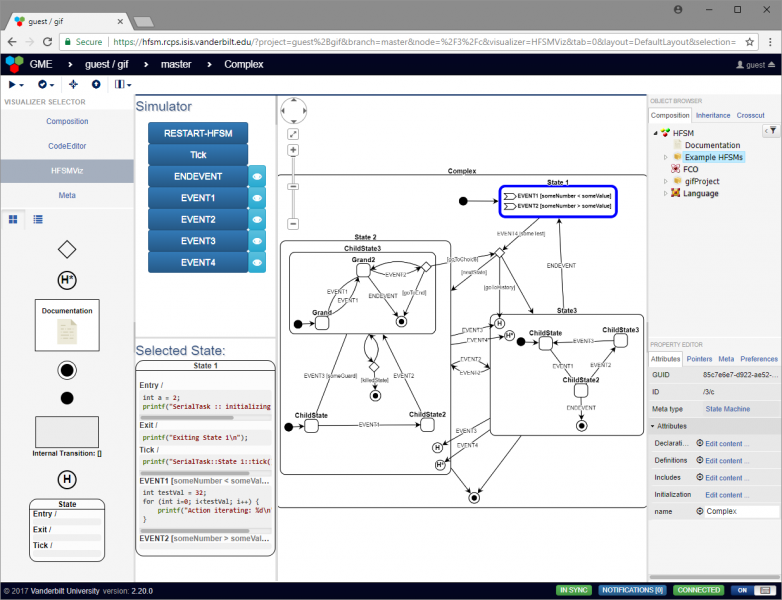
In addition to editing the HFSM through webgme, the HFSMViz can also be used. Open an HFSM and click on the HFSMViz on the left side of the screen to use this mode.
Components can be dragged into the visualizer just like in webgme, with addditional operations accessible via the right-click context menu
Simulating a HFSM
In the HFSMViz, the active state of the simulation is highlighted in red, and the user can press the event buttons to see how the state machine will react to that event. If any guards need to be evaluated, a modal dialog will pop up with options for the user to select which guard should evaluate to true at that time. The user has the option of canceling the transition by selecting None. In the case that the guards are associated with exit transitions of a choice pseudostate, the Default Transition will be shown as a guard choice with no text.
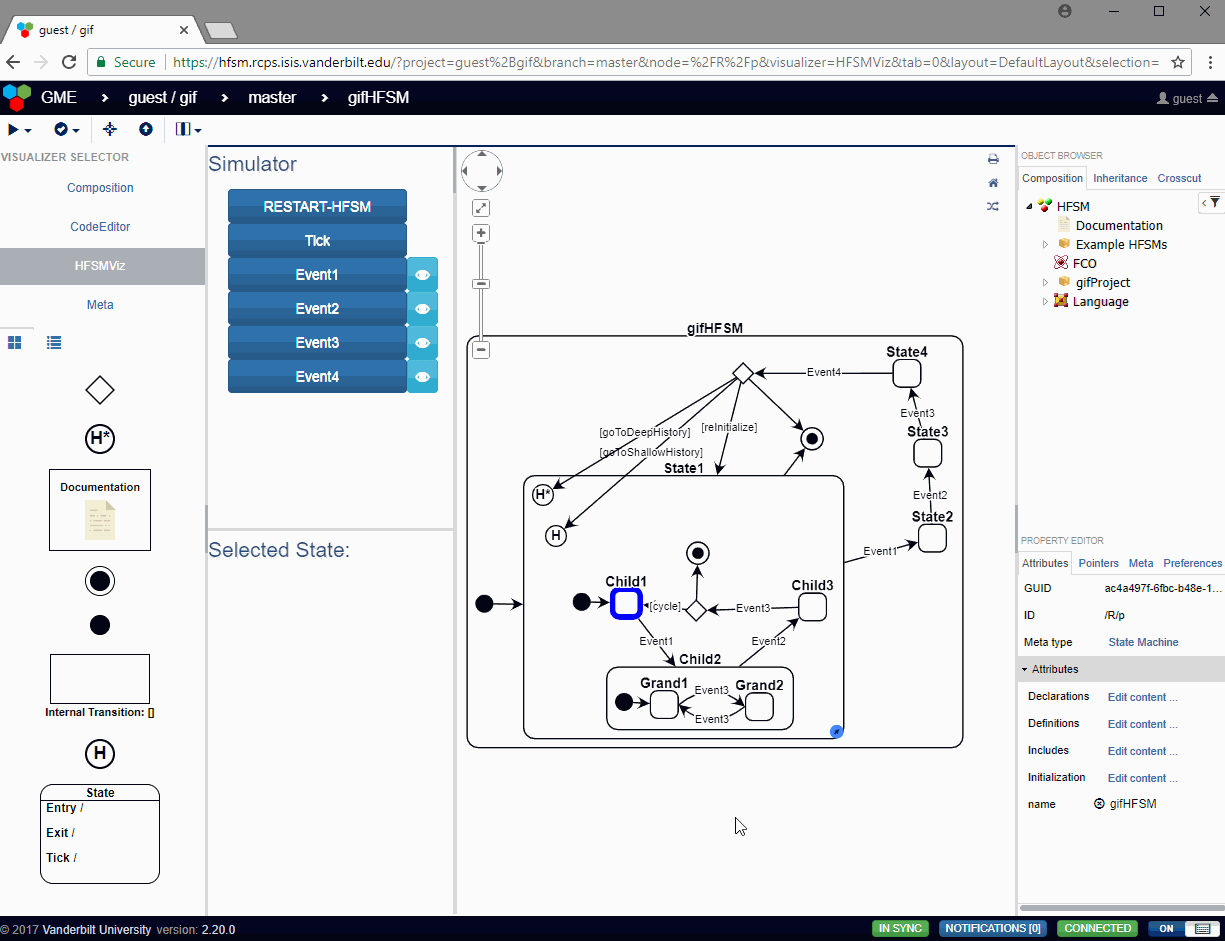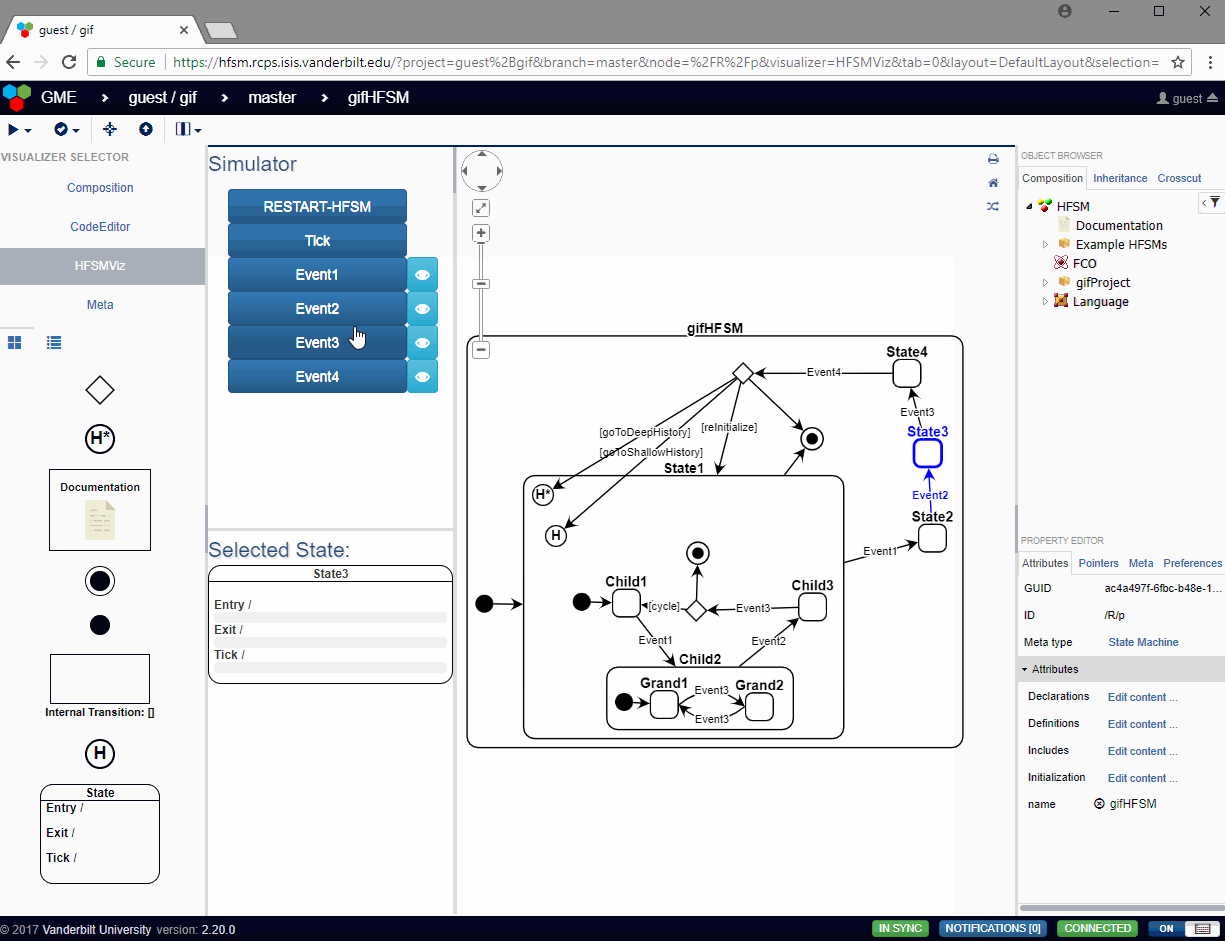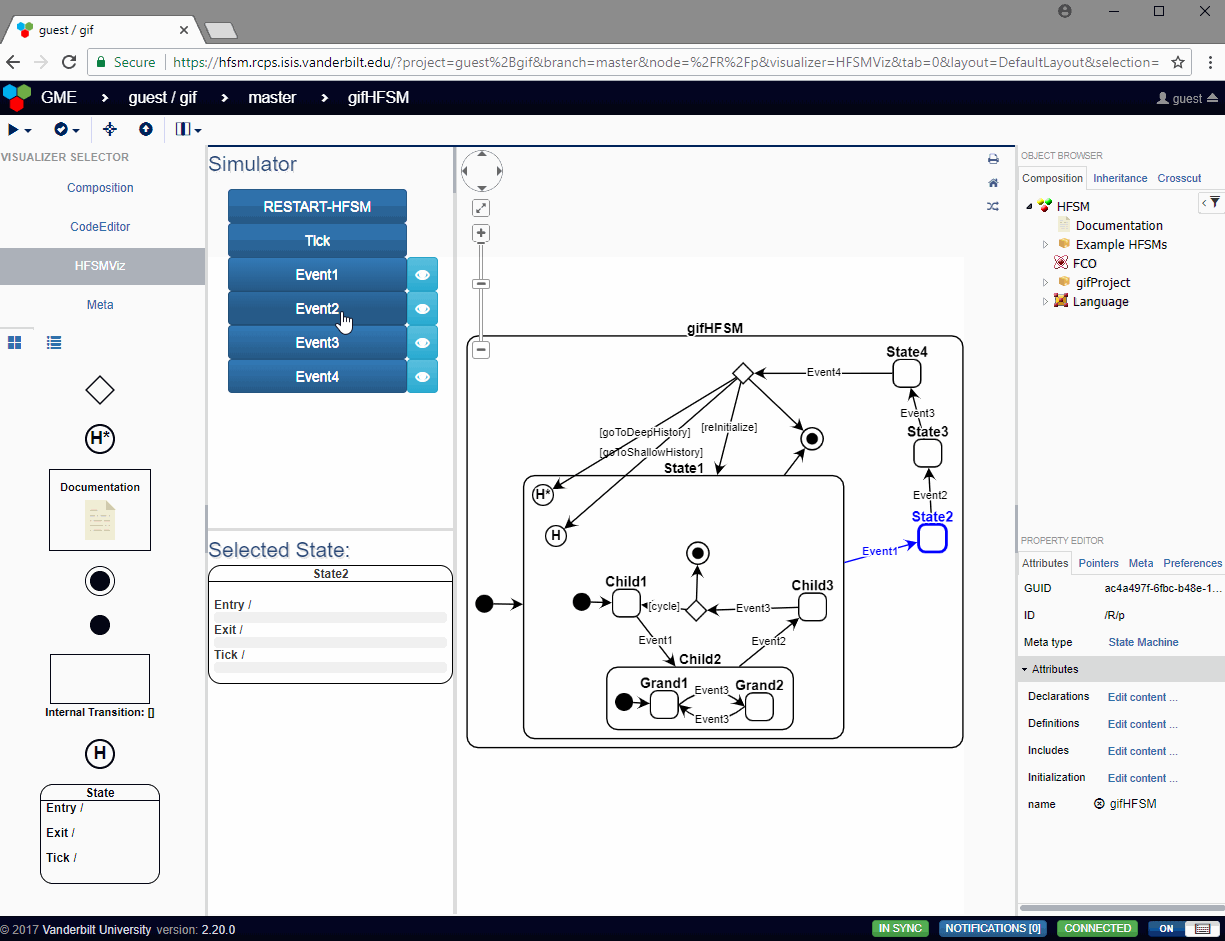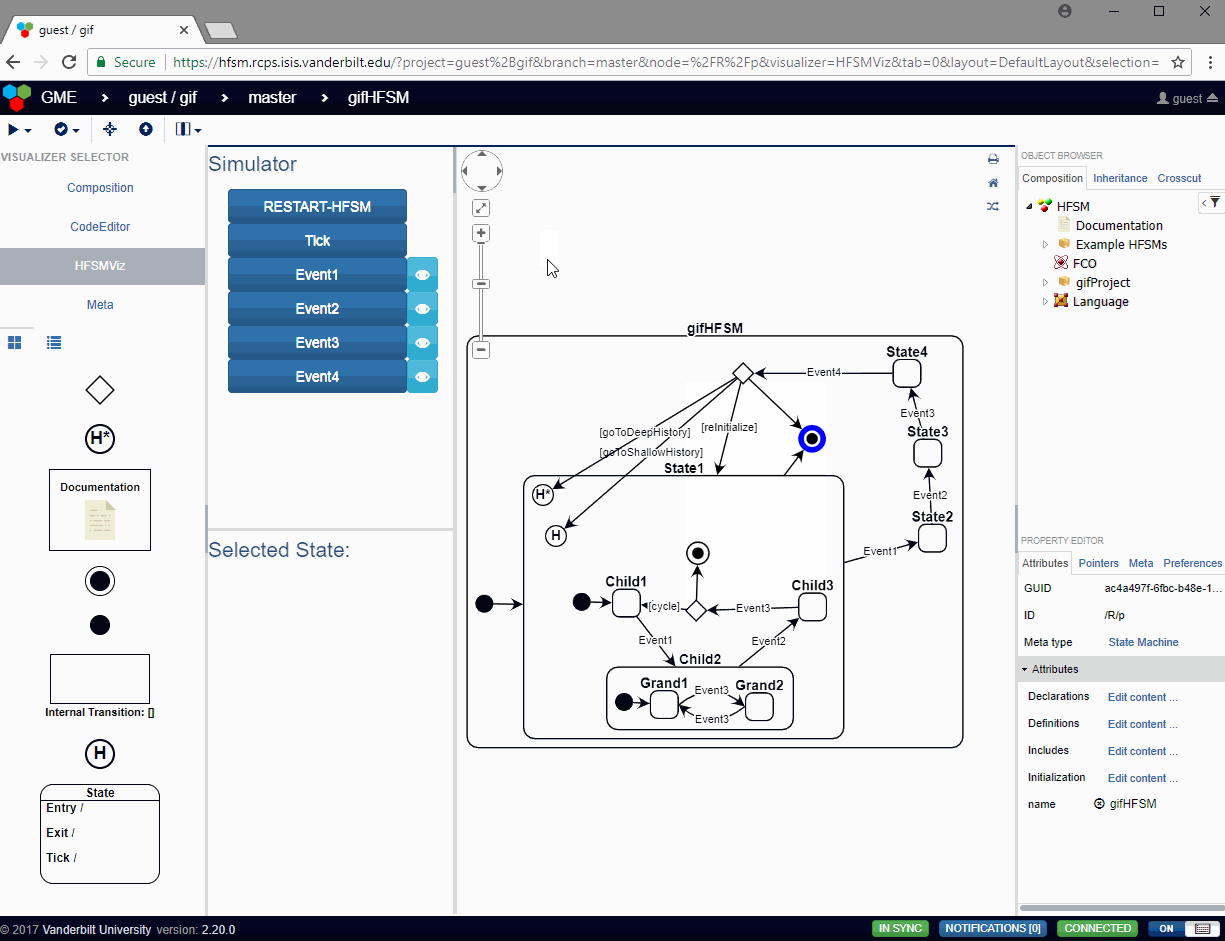
The HFSMViz visualizer allows the visualization of the full HFSM. It also provides:
- An interface to see which events will be handled by the HFSM when it is in a selected (or active) state
- Simulation of the HFSM which properly traverses the transitions from the currently active state to the next active state when the user spawns an event into the simulation.
- The visualization will even pop up dialogs asking the user which guard condition should be evalutated to true when the HFSM passes through a choice pseudostate or when multiple transitions have the same event trigger and different guards.
- Drag and drop external transition creation between two nodes of the HFSM
- Automatic layout and routing of the edges and nodes of the HFSM tree
- Context menu allowing the user to:
- Toggle the display of a state's children
- Set the active
- Add a new element (which can also be done by dragging from the
Part Browserand dropping onto the visualizer.
Code Generation
The SoftwareGenerator plugin supports generation of a Project and it's State Machines into executable code, with the option of generating test-bench code for interactively testing out the generated HFSM and tracing through which actions occur in what order when an event is spawned.
You can edit the code attributes for the State Machines, States, Internal Transitions, and External Transitions within the CodeEditor visualizer.
Test Bench Code
When the test code is generated, it generates a Makefile which builds a test and DEBUG target for each of the State Machines in the Project from which the plugin was executed. These test bench codes compile in (using a preprocessor define DEBUG_OUTPUT) logging code which traces when transitions are fired, which guards are true, which actions are executed, and which events are in the State Machine's event queue.
Example Test Bench Output for the Complex Example State Machine
jebKerman@ubuntu ~/webgme-hfsm/exampleHFSM make run_Complex_test_DEBUG
Compiling Complex_test_DEBUG
g++ -o Complex_test_DEBUG Complex_test.cpp Complex_GeneratedStates.cpp -O3 -std=c++14 -MD -MP -MF .dep/Complex_test_DEBUG.d -DDEBUG_OUTPUT
Running Complex_test_DEBUG
./Complex_test_DEBUG
INITIAL TRANSITION::ACTION for /3/c/m
ENTRY::Complex::State_1::/3/c/Y
SerialTask :: initializing State 1
Select which event to spawn:
0. ENDEVENT
1. EVENT1
2. EVENT2
3. EVENT3
4. EVENT4
5. INPUTEVENT
6. None
selection: 1
[ EVENT1 ]
GUARD [ someNumber < someValue ] for INTERNAL TRANSITION:/3/c/Y/t evaluated to TRUE
Action iterating: 0
Action iterating: 1
Action iterating: 2
Action iterating: 3
Action iterating: 4
Action iterating: 5
Action iterating: 6
Action iterating: 7
Action iterating: 8
Action iterating: 9
Action iterating: 10
Action iterating: 11
Action iterating: 12
Action iterating: 13
Action iterating: 14
Action iterating: 15
Action iterating: 16
Action iterating: 17
Action iterating: 18
Action iterating: 19
Action iterating: 20
Action iterating: 21
Action iterating: 22
Action iterating: 23
Action iterating: 24
Action iterating: 25
Action iterating: 26
Action iterating: 27
Action iterating: 28
Action iterating: 29
Action iterating: 30
Action iterating: 31
Handled EVENT1
Select which event to spawn:
0. ENDEVENT
1. EVENT1
2. EVENT2
3. EVENT3
4. EVENT4
5. INPUTEVENT
6. None
selection: 4
[ EVENT4 ]
GUARD [ someTest ] for EXTERNAL TRANSITION:/3/c/I evaluated to TRUE
NO GUARD on EXTERNAL TRANSITION:/3/c/o
EXIT::Complex::State_1::/3/c/Y
Exiting State 1
TRANSITION::ACTION for /3/c/I
TRANSITION::ACTION for /3/c/o
ENTRY::Complex::State3::/3/c/T
TRANSITION::ACTION for /3/c/T/I
ENTRY::Complex::State3::ChildState::/3/c/T/W
STATE TRANSITION: Complex::State_1->Complex::State3::ChildState
Handled EVENT4
Select which event to spawn:
0. ENDEVENT
1. EVENT1
2. EVENT2
3. EVENT3
4. EVENT4
5. INPUTEVENT
6. None
selection: 1
[ EVENT1 ]
NO GUARD on EXTERNAL TRANSITION:/3/c/T/L
EXIT::Complex::State3::ChildState::/3/c/T/W
TRANSITION::ACTION for /3/c/T/L
ENTRY::Complex::State3::ChildState2::/3/c/T/0
STATE TRANSITION: Complex::State3::ChildState->Complex::State3::ChildState2
Handled EVENT1
Select which event to spawn:
0. ENDEVENT
1. EVENT1
2. EVENT2
3. EVENT3
4. EVENT4
5. INPUTEVENT
6. None
selection: 2
[ EVENT2 ]
NO GUARD on EXTERNAL TRANSITION:/3/c/T/j
EXIT::Complex::State3::ChildState2::/3/c/T/0
TRANSITION::ACTION for /3/c/T/j
ENTRY::Complex::State3::ChildState3::/3/c/T/w
STATE TRANSITION: Complex::State3::ChildState2->Complex::State3::ChildState3
Handled EVENT2
Select which event to spawn:
0. ENDEVENT
1. EVENT1
2. EVENT2
3. EVENT3
4. EVENT4
5. INPUTEVENT
6. None
selection: 3
[ EVENT3 ]
NO GUARD on EXTERNAL TRANSITION:/3/c/T/p
EXIT::Complex::State3::ChildState3::/3/c/T/w
TRANSITION::ACTION for /3/c/T/p
ENTRY::Complex::State3::ChildState::/3/c/T/W
STATE TRANSITION: Complex::State3::ChildState3->Complex::State3::ChildState
Handled EVENT3
Select which event to spawn:
0. ENDEVENT
1. EVENT1
2. EVENT2
3. EVENT3
4. EVENT4
5. INPUTEVENT
6. None
selection: 4
[ EVENT4 ]
NO GUARD on EXTERNAL TRANSITION:/3/c/w
EXIT::Complex::State3::ChildState::/3/c/T/W
EXIT::Complex::State3::/3/c/T
TRANSITION::ACTION for /3/c/w
ENTRY::Complex::State_2::/3/c/v
ENTRY::Complex::State_2::ChildState::/3/c/v/K
STATE TRANSITION: Complex::State3->Complex::State_2::Deep_History_Pseudostate
Handled EVENT4
Select which event to spawn:
0. ENDEVENT
1. EVENT1
2. EVENT2
3. EVENT3
4. EVENT4
5. INPUTEVENT
6. None
selection: 4
[ EVENT4 ]
NO GUARD on EXTERNAL TRANSITION:/3/c/Q
EXIT::Complex::State_2::ChildState::/3/c/v/K
EXIT::Complex::State_2::/3/c/v
TRANSITION::ACTION for /3/c/Q
ENTRY::Complex::State3::/3/c/T
ENTRY::Complex::State3::ChildState::/3/c/T/W
STATE TRANSITION: Complex::State_2->Complex::State3::Deep_History_Pseudostate
Handled EVENT4
Select which event to spawn:
0. ENDEVENT
1. EVENT1
2. EVENT2
3. EVENT3
4. EVENT4
5. INPUTEVENT
6. None
selection: 6
Finished
Examples
Example HFSMs included in the Samples Seed:
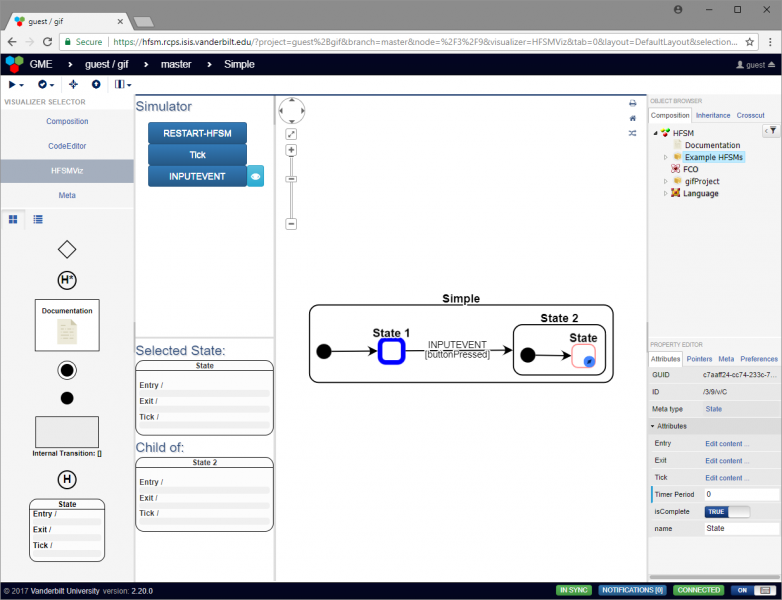
Simple:
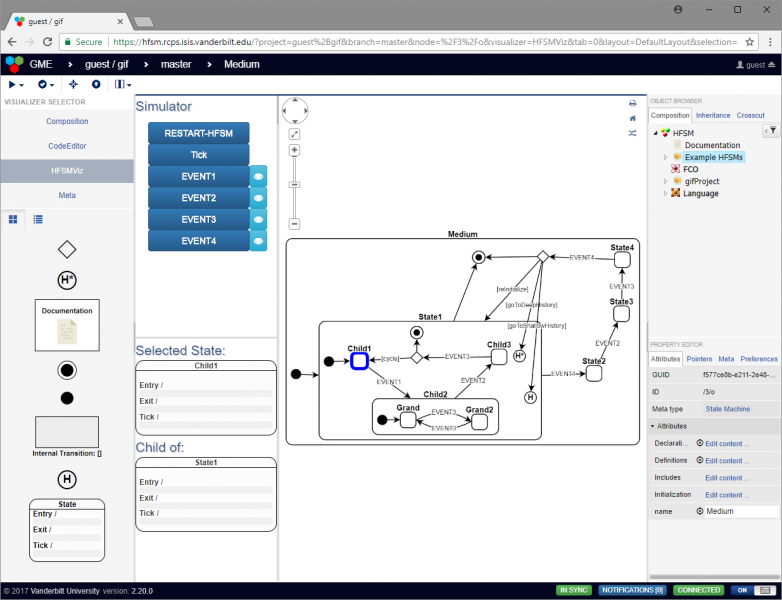
Medium:
Complex: