The terms denote engineering domains that have high CPS content.
file
We present a bifurcation analysis of electrical alternans in the two-current Mitchell-Schaeffer (MS) cardiac-cell model using the theory of 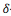 -decidability over the reals. Electrical alternans is a phenomenon characterized by a variation in the successive Action Potential Durations (APDs) generated by a single cardiac cell or tissue.
-decidability over the reals. Electrical alternans is a phenomenon characterized by a variation in the successive Action Potential Durations (APDs) generated by a single cardiac cell or tissue.
file
This project is a modular multi-robot cyber-physical system (CPS) for assisting young developmentally-delayed children learn to walk. The challenges of assisting young developmentally-delayed children learn to walk are 1) stabilizing medio-lateral body movement; and 2) developing gait that exploits potential and kinetic energy exchange. Typically, adults help children learn to walk by providing support that enables them to safely explore the environment.
file
This post considers a problem of target or source localization based on the measurements from a mobile sensor or a network of sensors. The assumption is that the received signal strength is strictly monotonic with the distance between the target and the sensor. No explicit signal propagation model, neither the structure nor the mathematical description, is assumed or used in localization. It shows that this mere knowledge of monotonicity suffices in locating the unknown target in the absence of noise.
file
Optimization algorithms used in a real-time and safety-critical context offer the potential for considerably advancing robotic and autonomous systems by improving their ability to execute complex missions. However, this promise cannot happen without proper attention to the considerably stronger operational constraints that real time, safety-critical applications must meet, unlike their non-real-time, desktop counterparts.
file
This exhibition presents two projects. The first project is a framework and associated tooling for the extraction of system specifications from test data that has been automatically generated from automated executions of the system. The test data in our framework consists of sequences of inputs to and the corresponding outputs from the system. From an initial collection of test data, data-mining techniques are used to infer the invariants; then the system is instrumented with the invariants and new test data is generated to try to invalidate the mined invariants.
file
Part 1: Upper-limb motor impairments arise from a wide range of clinical conditions including amputations, spinal cord injury, or stroke. Addressing lost hand function, therefore, is a major focus of rehabilitation interventions; and research in robotic hands and hand exoskeletons aimed at restoring fine motor control functions gained significant speed recently. Integration of these robots with neural control mechanisms is also an ongoing research direction.
file
We transitioned from a tethered system to a fully wearable mobile one, which is suitable for clinical applications. We designed the textile components of the exosuit to provide unilateral assistance to the paretic limb of persons poststroke during walking. The suit provides partial assistance to ankle dorsiflexion (DF) and ankle plantarflexion (PF) and encourages a more symmetric and natural gait. The results of our treadmill-based study show that the exosuit could improve interlimb propulsion symmetry and ankle kinematics of seven chronic poststroke patients.
file
Large scale applications of cyber physical systems (CPS) such as commercial buildings with Building Automation System (BAS)-based demand response (DR) can play a key role in alleviating demand peaks and associated grid stress, increased electricity unit cost, and carbon emissions. However, benefits of BAS alone are often limited because their demand peak reduction cannot be maintained long enough without unduly affecting occupant comfort. This project seeks to develop control algorithms to closely integrate battery storage-based DR with existing BAS capabilities.